add:https://www.blackmoreops.com/2014/06/18/sysstat-sar-examples-usage/
sysstat – SAR examples and usage
This first part describes SAR examples and usage along with installation.
Step 1. Install sysstat Package
sysstat is usually not installed in Linux system by default. You need to install it. You also need to make sure you have the correct repositories added. As I personally use Kali Linux, I’ve added Kali Linux
official repositories. Follow your distro documentation to add yours. But it is pretty straight forward.
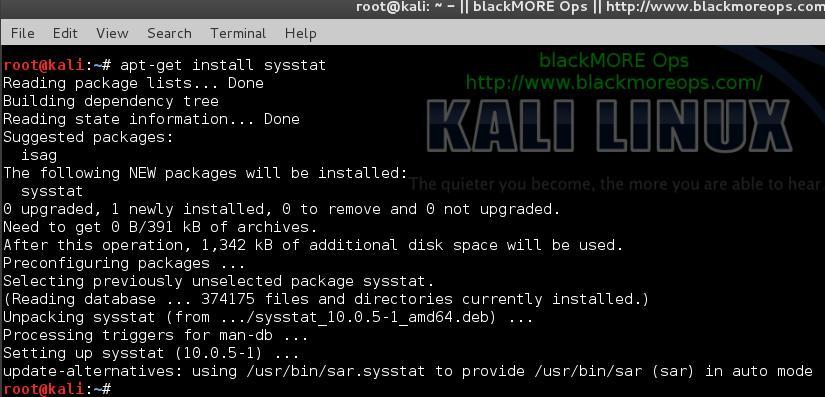
To install sysstat package:
sudo apt-get install sysstat
(or)
yum install sysstat
(or)
rpm -ivh sysstat-10.0.0-1.i586.rpm
Step 2. Enable stat collection
In new systems once you’ve installed sysstat, it enables statistics collections by default. In case it is not you can enable it by editing 1 word in the following file:
vi /etc/default/sysstat
Change ENABLED=”false” to ENABLED=”true”
#
# Default settings for /etc/init.d/sysstat, /etc/cron.d/sysstat
# and /etc/cron.daily/sysstat files
#
# Should sadc collect system activity informations? Valid values
# are "true" and "false". Please do not put other values, they
# will be overwritten by debconf!
ENABLED="true"
Save the file. Restart sysstat.
service sysstat restart
(or)
/etc/init.d/sysstat restart
Once it’s restarted, it will start collecting data.
Step 3. Changing collection intervals
Default sysstat configuration collects data every 10 minutes. You can change it easily. If you got a fast system or you need more intensive monitoring of your system (i.e. a web server with enough RAM and Processor), then you might want to reduce the collection interval from 10 minutes to 2 minutes. Alternatively, you can change it to 15 minutes if you got a slow system. Either way, it’s easy to do and here are the steps:
vi /etc/cron.d/sysstat
# The first element of the path is a directory where the debian-sa1
# script is located
PATH=/usr/lib/sysstat:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
# Activity reports every 10 minutes everyday
5-55/10 * * * * root command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/null && debian-sa1 1 1
# Additional run at 23:59 to rotate the statistics file
59 23 * * * root command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/null && debian-sa1 60 2
Change
5-55/10 * * * * root command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/null && debian-sa1 1 1
To
*/2 * * * * root command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/null && debian-sa1 1 1
Save the file and restart sysstat.
service sysstat restart
(or)
/etc/init.d/sysstat restart
Step 4. Check sysstat version
Once installed, verify the sar version using the following command:
root@kali:~# sar -V
sysstat version 10.0.5
(C) Sebastien Godard (sysstat orange.fr)